Cognitive psychology is the study of mental processes such as perception, memory, problem-solving, and decision-making, focusing on how people acquire, process, and store information.
Ever feel like your mind is working against you? Negative thoughts, self-doubt, and unhelpful habits can hold you back from reaching your full potential. But what if you could rewire your brain to think differently, make better decisions, and cultivate a mindset built for growth?
That’s where cognitive psychology comes in. It’s the science of how we think, learn, and process information. Shaping everything from our daily habits to our long-term success. By understanding and applying simple cognitive psychology hacks. You can train your brain to overcome mental roadblocks, develop resilience, and create lasting positive change.
In this post, we’ll dive into powerful cognitive techniques that help you challenge negative thought patterns, reframe your perspective, and boost your motivation. Whether you want to build confidence, break free from limiting beliefs, or simply think more effectively, these mindset hacks will set you on the right path. Let’s get started!
Headlines
Understanding the Power of Cognitive Psychology in Mindset-Shaping
- The Role of Cognitive Psychology Biases in Mindset
- The Science of Neuroplasticity: Rewiring Your Brain for Growth
Practical Cognitive Psychology Hacks for Personal Growth
- Cognitive Restructuring: Reframing Negative Thoughts
- The Power of Metacognition: Thinking About Your Thinking
Building a Resilient Mindset Through Cognitive Psychology
Understanding the Power of Cognitive Psychology in Mindset-Shaping
The Role of Cognitive Psychology Biases in Mindset
Your brain is constantly processing information, making decisions, and forming beliefs—often without you even realizing it. While this mental automation helps you navigate daily life. It can also lead to cognitive psychology biases, which are systematic thinking errors that distort reality. These biases shape how you see yourself, others, and the world around you, directly influencing your mindset and personal growth.
Understanding cognitive psychology biases is crucial because they can either fuel self-improvement or reinforce limiting beliefs. By recognizing and managing them, you can take control of your thoughts and develop a more balanced, growth-oriented mindset.
Common Cognitive Biases That Impact Mindset
- Negativity Bias: Why Your Brain Focuses on the Worst
The human brain has a built-in tendency to give more weight to negative experiences than positive ones. This evolutionary trait helped our ancestors survive by remembering dangers. But in modern life, it often manifests as self-doubt, fear of failure, and overthinking mistakes. Mindset Shift: Instead of dwelling on setbacks, practice cognitive restructuring by reframing failures as learning experiences. Consciously remind yourself of past successes to balance out your perspective. - Confirmation Bias: Seeing What You Expect to See
If you believe something about yourself—whether positive or negative—your brain will actively seek out evidence to confirm that belief. If you think, “I’m not good at public speaking,” you’ll focus on every nervous moment while ignoring times when you spoke confidently.Mindset Shift: Challenge your assumptions. Ask yourself, What evidence do I have that contradicts this belief? Keep a journal of small wins to train your brain to recognize progress. - Self-Serving Bias: Taking Credit for Wins, Blaming Others for Losses
This bias makes it easier to credit personal success to effort and skill but blame failure on external factors. While protecting self-esteem, it can also prevent self-awareness and growth.Mindset Shift: Take responsibility for both your wins and losses. Instead of blaming circumstances, ask, What can I learn from this? A growth mindset thrives on continuous improvement.
Overcoming Cognitive psychology Biases for a Growth-Oriented Mindset
Recognizing cognitive psychology biases is the first step toward rewiring your thinking. Here are some cognitive psychology hacks to help shift your mindset:
- Practice Mindful Awareness: Regularly pause and analyze your thoughts. Are they based on facts, or are biases distorting them?
- Use the Opposite Test: If you hold a belief, consider what the opposite perspective might look like. This broadens your thinking and reduces bias.
- Adopt a Scientist’s Mindset: View your thoughts as hypotheses rather than facts. Be willing to experiment and adjust based on real evidence.
By actively managing cognitive psychology biases, you can break free from limiting beliefs, see challenges as opportunities, and develop a strong, resilient mindset that supports personal growth.
The Science of Neuroplasticity: Rewiring Your Brain for Growth
Your brain is not a fixed, unchangeable structure, it’s a dynamic system capable of learning, adapting, and evolving throughout your life. This ability, known as neuroplasticity, is what allows you to develop new habits, reframe negative thought patterns, and ultimately transform your mindset for personal growth.
By intentionally engaging in specific mental exercises and behaviors, you can rewire your brain to support self-improvement, resilience, and success. Understanding how neuroplasticity works and how to harness it can give you the power to break free from limiting beliefs and unlock your full potential.
How Neuroplasticity Works
At its core, neuroplasticity is the brain’s ability to reorganize itself by forming and strengthening new neural connections. Every time you think a thought, learn a new skill, or engage in a habit, your brain’s neurons fire together, reinforcing specific pathways. This is often summed up by the phrase:
🧠 “Neurons that fire together, wire together.”
This means that the more you practice a certain thought pattern or behavior, the stronger the neural pathways associated with it become. If you frequently engage in self-doubt, those pathways become more ingrained. But if you intentionally practice self-confidence and positive thinking, your brain strengthens those alternative pathways, making them the default mode of thinking over time.
Rewiring Your Brain for a Growth Mindset
To leverage neuroplasticity for personal growth, you must consciously train your brain to adopt thoughts, habits, and behaviors that align with success. Here’s how:
1. Challenge and Reframe Negative Thought Patterns
Your thoughts shape your reality. If you constantly tell yourself, “I’m not good at this,” your brain reinforces that belief. However, by practicing cognitive restructuring, you can replace limiting beliefs with empowering ones.
🔹 Try this: The next time you catch yourself in a negative thought, pause and ask: Is this belief true? What evidence do I have to support or refute it? Then, reframe the thought to something constructive, such as:
👉 “I may struggle with this now, but I can improve with practice.”
Over time, this practice rewires your brain to default to a positive, growth-oriented perspective.
2. Strengthen Neural Pathways Through Repetition and Habit Formation
The more you engage in a behavior, the more automatic it becomes. This is why building positive habits is essential for long-term personal growth.
🔹 Try this: Choose one habit that aligns with your goals—whether it’s journaling, exercising, or daily affirmations—and commit to it consistently. Start small, but be consistent, as repetition is what strengthens neural connections.
👉 Example: If you want to become more optimistic, practice gratitude daily by writing down three things you’re grateful for. Over time, your brain will naturally focus on the positives instead of defaulting to negativity.
3. Use Visualization to Reinforce Neural Pathways
Your brain doesn’t differentiate between real and vividly imagined experiences. When you visualize success, the same neural circuits activate as if you were actually experiencing it.
🔹 Try this: Spend a few minutes each day visualizing yourself achieving a personal growth goal. Imagine how it feels, what it looks like, and the actions you take to get there. This helps your brain form the necessary neural connections to make that vision a reality.
Final Thoughts: Embracing Neuroplasticity for Lifelong Growth
The power to change your mindset and achieve growth is literally in your hands—or rather, in your brain. By understanding and applying neuroplasticity, you can:
Break free from self-limiting beliefs
Create thought patterns that support success
Develop positive habits that reinforce personal growth
Change doesn’t happen overnight, but with intentional effort and consistency, you can rewire your brain to think, feel, and behave in ways that align with your highest potential. Your brain is always adapting—make sure it’s adapting in the direction of growth.
Practical Cognitive Psychology Hacks for Personal Growth
Cognitive Restructuring: Reframing Negative Thoughts
Your thoughts shape your emotions, behaviors, and overall mindset. If you constantly engage in negative self-talk or allow limiting beliefs to take over, it can hold you back from achieving personal growth. Cognitive restructuring is a psychological technique that helps you identify, challenge, and replace these negative thought patterns with more balanced and constructive ones.
Developed as part of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), cognitive restructuring empowers you to take control of your thinking instead of letting automatic, unhelpful thoughts dictate your actions. This process is essential for shifting toward a growth-oriented mindset and fostering resilience.
Recognizing Negative Thought Patterns
The first step in cognitive restructuring is becoming aware of the negative thoughts that influence your mindset. Many people experience distorted thinking without realizing it. Some of the most common patterns include:
- All-or-Nothing Thinking: Seeing situations in extreme categories, such as “I always fail” or “I’m never good enough,” instead of recognizing progress or middle ground.
- Catastrophizing: Assuming the worst will happen, even when there is little evidence to support it.
- Personalization: Blaming yourself for external events beyond your control, leading to unnecessary guilt and self-criticism.
- Overgeneralization: Drawing broad conclusions from a single negative experience, such as “I failed once, so I’ll always fail.”
- Mental Filtering: Focusing only on the negative aspects of a situation while ignoring any positives.
Identifying these thought patterns allows you to challenge them rationally rather than accepting them as facts.
Challenging and Reframing Negative Thoughts
Once you recognize a negative thought, the next step is to question its accuracy. Ask yourself:
- What evidence supports or contradicts this thought?
- Am I making assumptions or jumping to conclusions?
- How would I view this situation if a friend were experiencing it?
- Is there a more balanced, realistic way to interpret this event?
For example, if you catch yourself thinking, “I always mess things up,” challenge it by recalling times when you succeeded. A more constructive way to reframe this might be: “I’ve had setbacks, but I’ve also had many successes. I can learn from mistakes and improve.”
This shift does not mean ignoring difficulties or pretending everything is positive, but rather adopting a realistic and empowering perspective that promotes growth.
Practicing Cognitive Restructuring for Long-Term Change
Reframing negative thoughts requires consistent practice. Here are some effective strategies to reinforce this habit:
- Journaling: Write down negative thoughts and actively work on restructuring them. Over time, you will notice patterns and develop stronger cognitive awareness.
- Mindfulness and Self-Compassion: Observe your thoughts without judgment. Instead of reacting emotionally, pause and consider whether a thought is helpful or needs restructuring.
- Affirmations and Positive Self-Talk: Replace self-defeating statements with encouraging ones that reflect a balanced reality. Instead of saying, “I’ll never be good at this,” try “I am improving with effort and practice.”
- Cognitive Distancing: Remind yourself that thoughts are not always facts. Just because you think something does not mean it is true. Create space between yourself and your automatic responses.
Cognitive restructuring is a powerful tool for changing the way you perceive challenges, setbacks, and even your own abilities. By consistently applying this technique, you can train your brain to focus on growth, resilience, and constructive thinking, leading to lasting improvements in mindset and personal development.
The Power of Metacognition: Thinking About Your Thinking
Metacognition, often described as “thinking about thinking,” is the ability to become aware of and control your thought processes. It involves reflecting on how you think, why you think the way you do, and whether your thought patterns are helping or hindering your growth. By practicing metacognition, you can gain greater insight into your cognitive psychology habits, enabling you to make more deliberate and effective decisions, ultimately leading to a more constructive mindset.
In the context of personal growth and mindset improvement, metacognition provides a powerful tool for enhancing self-awareness and emotional intelligence. It helps you assess your cognitive psychology responses to various situations, enabling you to adjust them to better align with your goals and values. This awareness not only fosters better decision-making but also helps you manage stress, overcome obstacles, and sustain motivation during challenging times.
Understanding Your Thinking Patterns
To effectively practice metacognition, it’s essential to start by observing your thought processes. Often, people operate on “autopilot,” reacting to situations without much reflection. Metacognitive awareness encourages you to step back and ask questions like:
- What am I thinking right now, and why?
- Are my thoughts based on facts, or am I interpreting the situation through a biased lens?
- How do my thoughts influence my emotions and behaviors?
- Are there alternative ways to think about this situation that might be more helpful?
By regularly pausing to ask yourself these questions, you cultivate an understanding of how your thoughts impact your emotional state, decisions, and actions. This process helps you break free from automatic, habitual responses and shift toward more intentional, mindful thinking.
Improving Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
Metacognition plays a crucial role in enhancing decision-making. When faced with choices, many people rely on impulse or habit without considering the broader consequences. Metacognitive thinking encourages a more deliberate approach to decision-making, where you actively assess the situation, consider different perspectives, and weigh possible outcomes.
For example, if you’re deciding whether to take on a new project, instead of making a snap judgment, you might ask yourself:
- What are the potential benefits and drawbacks of this decision?
- How do I feel about taking on this task, and why?
- What might be the long-term impact on my goals and well-being?
By reflecting on these questions, you’re engaging in metacognitive problem-solving, which can lead to more informed and balanced choices. This approach prevents impulsive decisions driven by emotion or external pressure, replacing them with choices based on thoughtful reflection and a clear understanding of your values and priorities.
Enhancing Emotional Regulation
Metacognition is also closely linked to emotional regulation. When you practice thinking about your thinking, you become more aware of how certain thoughts trigger emotional reactions. For instance, if you catch yourself thinking negatively about a challenging situation, you might recognize that this thought is increasing your anxiety or frustration. With this awareness, you can intervene by either changing your thought pattern or adopting strategies to regulate your emotional response.
Metacognitive strategies like self-reflection and cognitive psychology distancing help you break the cycle of automatic emotional reactions. By stepping back from a situation and evaluating your thoughts, you gain greater control over your emotions, leading to more stable and grounded responses in stressful or challenging circumstances.
Using Metacognition for Goal Achievement
Metacognition also plays a vital role in the pursuit of personal growth goals. When working toward a goal, it’s common to encounter obstacles or moments of self-doubt. Metacognitive thinking allows you to reflect on your progress, adjust your strategies, and remain flexible when things don’t go as planned.
For instance, if you’re working on developing a healthier lifestyle but find yourself slipping back into old habits, metacognition can help you identify the thought patterns driving this behavior. You might recognize that you’re falling into negative self-talk, such as “I’ll never stick to this” or “I don’t have the willpower.” By becoming aware of these thoughts, you can challenge them and replace them with more constructive beliefs, like “I’ve made progress, and setbacks are a part of the process.”
Moreover, metacognition encourages you to evaluate your approach to achieving goals and refine your methods as needed. Are your strategies effective? Are you staying motivated? What adjustments can you make to get back on track? By asking these reflective questions, you stay focused and adaptable, enhancing your chances of success.
Developing Metacognitive Practices
To integrate metacognition into your daily life, consider these practices:
- Mindful Journaling: Regularly write about your thoughts, feelings, and experiences. Reflect on the reasoning behind your thoughts and behaviors, and assess whether they align with your long-term goals.
- Think-Aloud Technique: When solving problems or making decisions, verbalize your thought process. This practice can help you clarify your reasoning, spot flaws in your logic, and consider alternative viewpoints.
- Mindfulness Meditation: Engage in meditation to observe your thoughts without judgment. This practice increases awareness of your mental processes, making it easier to reflect on and adjust your thinking patterns.
By incorporating metacognitive practices into your routine, you build the foundation for a self-aware, adaptable, and growth-oriented mindset. This heightened awareness of your thinking processes will not only enhance your personal growth but also provide you with the tools to overcome obstacles and thrive in the face of challenges.
Building a Resilient Mindset Through Cognitive Psychology
Habit Formation and Thought Patterns
Metacognition plays a significant role in habit formation and the development of thought patterns that either propel or hinder personal growth. While habits are the automatic behaviors that shape our daily lives, thought patterns are the mental frameworks that guide those behaviors. The power of metacognition lies in its ability to create awareness and control over both, allowing you to reshape your habits and transform your mindset in meaningful ways.
When you practice metacognition, you’re not only reflecting on your thoughts but also examining the underlying patterns that drive them. This awareness enables you to consciously modify how you think and act, promoting positive change over time. By consciously reflecting on your habits and the thought processes that reinforce them, you can break free from old, unproductive cycles and form new, empowering ones.
Understanding the Connection Between Thought Patterns and Habits
Habits and thought patterns are closely intertwined. Many of our automatic behaviors are driven by deeply ingrained beliefs, assumptions, and thought patterns. For example, if you consistently think “I can’t do this,” that belief may prevent you from even attempting a task, thereby forming a habit of avoidance. Conversely, if your habitual thought pattern is “I can handle this challenge,” your actions will more likely reflect a proactive, determined approach to the situation.
Metacognition helps you break this cycle by allowing you to recognize how certain thought patterns contribute to the formation or reinforcement of habits. It encourages you to examine your thoughts in a non-judgmental, objective way to identify the ones that are not serving you. With this insight, you can work to reframe these thoughts, which in turn will positively impact your habits.
For instance, you may realize that negative self-talk leads to procrastination. By practicing metacognitive reflection, you can change your perspective, replacing thoughts of doubt with affirmations of capability. As a result, you may notice a shift in behavior, such as increased motivation and follow-through, which will eventually form a new, productive habit.
Using Metacognition to Develop Positive Habits
To use metacognition effectively in habit formation, you must actively reflect on your existing habits and thought processes. Here’s how metacognition can help you develop more positive, lasting habits:
- Awareness of Current Habits and Thoughts: Begin by observing your current behaviors and the thoughts that accompany them. Take note of habits that you want to change and the thought patterns that drive them. For example, if you often find yourself procrastinating on important tasks, reflect on the thoughts that fuel this behavior—perhaps thoughts like “I’ll do it later” or “This is too hard.”
- Identify Unproductive Thought Patterns: Once you recognize the harmful thoughts contributing to your habits, the next step is to question and challenge these beliefs. Are they based on facts or assumptions? Are they helping you move toward your goals, or are they holding you back? By practicing metacognitive questioning, you can uncover and dismantle the thought patterns that undermine your success.
- Replace Negative Thought Patterns with Constructive Ones: After identifying negative or limiting thought patterns, replace them with healthier, more constructive alternatives. Instead of thinking “I’m terrible at this,” reframe your thinking to “I may not be perfect, but I can improve with practice.” This change in thought not only helps overcome mental blocks but also shapes new behaviors in alignment with your desired habit.
- Monitor Progress and Adjust as Needed: Habit formation takes time, and it’s essential to consistently monitor your thoughts and behaviors. As you work toward developing a positive habit, regularly reflect on your progress. Are the new thought patterns sticking? Are there any setbacks or challenges? This constant metacognitive reflection allows you to make necessary adjustments and refine your approach over time.
- Cultivate Patience and Persistence: Developing new habits takes consistent effort. Metacognition can help you remain patient and persistent by allowing you to notice small successes and reinforcing the belief that change is possible. By actively observing your journey, you can stay motivated.
Changing Thought Patterns to Overcome Negative Habits
Just as metacognition can help you form positive habits, it can also assist in overcoming negative ones. Negative habits often arise from recurring, automatic thoughts that lead to unhealthy behaviors. For example, a person may habitually overeat due to thoughts such as “I need comfort,” or “I can’t control myself.” These thought patterns create a cycle that reinforces the habit of overeating.
Metacognition offers a solution by allowing you to reflect on the thoughts that trigger these behaviors. You can begin by asking yourself questions like:
- Why do I feel the urge to overeat right now?
- What belief or thought is driving this behavior?
- How can I reframe this thought to prevent overeating?
For example, you might replace the thought “I can’t control myself” with “I have the power to make healthier choices, and I can start small.” By challenging these automatic, negative thoughts, you can gradually break the cycle of negative habits and create healthier alternatives.
The Role of Self-Compassion in Metacognition and Habit Change
An essential component of using metacognition to change habits is the practice of self-compassion. Many people are overly harsh on themselves when they don’t meet their goals, which can lead to feelings of failure and discouragement. Metacognition can help you adopt a more compassionate perspective by allowing you to reflect on mistakes in a constructive manner.
Instead of criticizing yourself for falling short, you can use metacognitive reflection to acknowledge the setback, assess what went wrong, and adjust your approach without judgment. By being kinder to yourself, you reduce the emotional barriers that often prevent habit change and make it easier to stay committed to your goals.
Conclusion: Harnessing Metacognition for Lasting Change
The power of metacognition lies in its ability to promote self-awareness, self-regulation, and deliberate action. By reflecting on your thought patterns, you gain control over the beliefs that drive your habits, enabling you to shift from unproductive behaviors to positive, growth-promoting habits. Whether you want to develop new habits or break old ones, metacognition gives you the tools to reframe your thoughts and create lasting change. As you continue to reflect, adjust, and refine your thinking, you set yourself up for long-term personal growth and success.
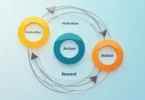
Using Dopamine and Motivation to Sustain Growth
Dopamine, often referred to as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter, plays a significant role in driving motivation, focus, and reward-based behavior. It’s a crucial element of the brain’s reward system and is heavily involved in creating and sustaining habits. Making it an essential component of personal growth. Understanding how dopamine works about motivation can empower you to leverage its power to keep moving toward your growth goals, even during challenging or stagnant periods.
The Role of Dopamine in Motivation
Dopamine is released in the brain when you experience something pleasurable or when you anticipate a reward. This release creates a feeling of satisfaction and reinforces behaviors that lead to positive outcomes. In the context of personal growth, dopamine is linked to motivation because it encourages you to repeat behaviors that produce rewards. When you accomplish a task or meet a goal, your brain releases dopamine, creating a sense of pleasure and achievement. This feeling motivates you to continue pursuing your objectives, as your brain starts associating progress with positive feelings.
For example, if you set a small goal, such as completing a workout or reading a chapter of a book, and you achieve it, your brain rewards you with a dopamine surge. This reward reinforces the behavior, making it more likely that you will continue to engage in the activity. Over time, this cycle of setting goals, experiencing rewards, and feeling motivated forms the foundation for sustained personal growth.
Dopamine and Habit Formation
One of the most powerful ways to leverage dopamine is through habit formation. Habits are essentially behaviors that are repeated so often that they become automatic, requiring less conscious effort over time. Dopamine plays a key role in this process, as it helps the brain associate specific actions with positive outcomes.
To effectively use dopamine in habit formation, it’s important to structure your goals and tasks in a way that maximizes the brain’s reward system. This can be done by:
- Setting Achievable Micro-Goals: Instead of aiming for large, intimidating objectives that may take time to achieve, break them down into smaller, more manageable goals. For example, instead of aiming to read an entire book, set a goal to read one chapter a day. Each time you meet that goal, your brain will release dopamine, which helps sustain your motivation over the long term.
- Celebrating Small Wins: Dopamine is not only released after completing significant goals but also in response to minor achievements. Acknowledge and celebrate small wins throughout your growth journey. This could be as simple as pausing to enjoy a moment of satisfaction or rewarding yourself with a treat or activity that makes you happy.
- Creating Positive Feedback Loops: The more frequently you achieve small goals, the more dopamine your brain will release. This creates a positive feedback loop that encourages you to keep moving forward. As your brain associates the behavior with rewards, the task becomes more ingrained, turning it into a habit. By stacking these micro-goals, you make progress toward your larger objective, while consistently receiving the motivation needed to continue.
The Role of Anticipation and Dopamine
Dopamine is not only released when rewards are received but also when rewards are anticipated. This element of anticipation is key to sustaining motivation. The mere thought of achieving a goal can trigger the release of dopamine, which drives you to take the necessary actions to reach that goal. This is why having a clear sense of purpose and regularly envisioning the outcome of your efforts can be a powerful motivator.
For instance, if you’re working toward a long-term personal growth goal, such as improving your health, visualizing the benefits of reaching that goal—feeling more energized, looking healthier, or achieving a higher level of fitness—can help stimulate dopamine release. The more vividly you anticipate the reward, the more motivated you are to take the steps necessary to achieve it.
Dopamine and Avoiding Burnout
While dopamine can be an incredible motivator, it’s important to balance its influence to avoid the risk of burnout. Overstimulating the dopamine system by constantly pursuing new goals without taking breaks or reflecting on progress can lead to mental and emotional exhaustion. To prevent this, it’s essential to incorporate periods of rest and recovery into your growth process.
One way to do this is by practicing delayed gratification, where you resist the impulse for immediate rewards and instead focus on long-term satisfaction. By spacing out the rewards and goals, you prevent the brain from becoming overstimulated and ensure that the motivation you gain from dopamine is sustained over a longer period. This approach can be particularly useful when working toward larger, more challenging personal growth goals.
Additionally, it’s important to recognize the role of dopamine tolerance. Just as the body can become accustomed to certain substances, the brain can develop a tolerance to dopamine’s effects. If you’re constantly seeking quick dopamine hits through easily accessible rewards—like social media notifications or junk food—it can diminish your motivation over time. To avoid this, focus on building healthy, sustainable habits that reward you in meaningful ways and create a lasting sense of accomplishment.
Practical Strategies for Using Dopamine to Sustain Motivation
- Gamify Your Growth Journey: Turn your personal growth process into a game by breaking down goals into smaller, manageable tasks and rewarding yourself when you complete them. The element of fun and challenge can amplify dopamine release and keep you motivated.
- Create a Reward System: Set up a system where you reward yourself for reaching specific milestones. For example, after a week of consistent exercise, treat yourself to something you enjoy, like a relaxing activity or a favorite snack. The anticipation of the reward can keep you motivated to stay on track.
- Track Progress and Visualize Success: Use visual trackers or journaling to track your progress and reflect on how far you’ve come. This helps maintain a sense of accomplishment, which sustains your motivation by reminding you of the rewards you’re working toward.
- Practice Gratitude: Incorporating gratitude into your routine can help increase dopamine levels by focusing your attention on positive experiences. When you actively acknowledge the things you’re grateful for, you cultivate a mindset that attracts motivation and growth.
Conclusion: Harnessing Dopamine for Sustained Personal Growth
Dopamine is a powerful tool in the pursuit of personal growth. By understanding its role in motivation, habit formation, and reward-seeking behavior, you can leverage this neurotransmitter to maintain momentum as you work toward your goals. Whether you’re tackling small tasks or striving for large, transformative changes, dopamine can serve as an engine that fuels your motivation. By structuring your growth journey in a way that incorporates achievable goals, rewards, and positive anticipation, you ensure that your pursuit of self-improvement is not only sustainable but also deeply fulfilling.